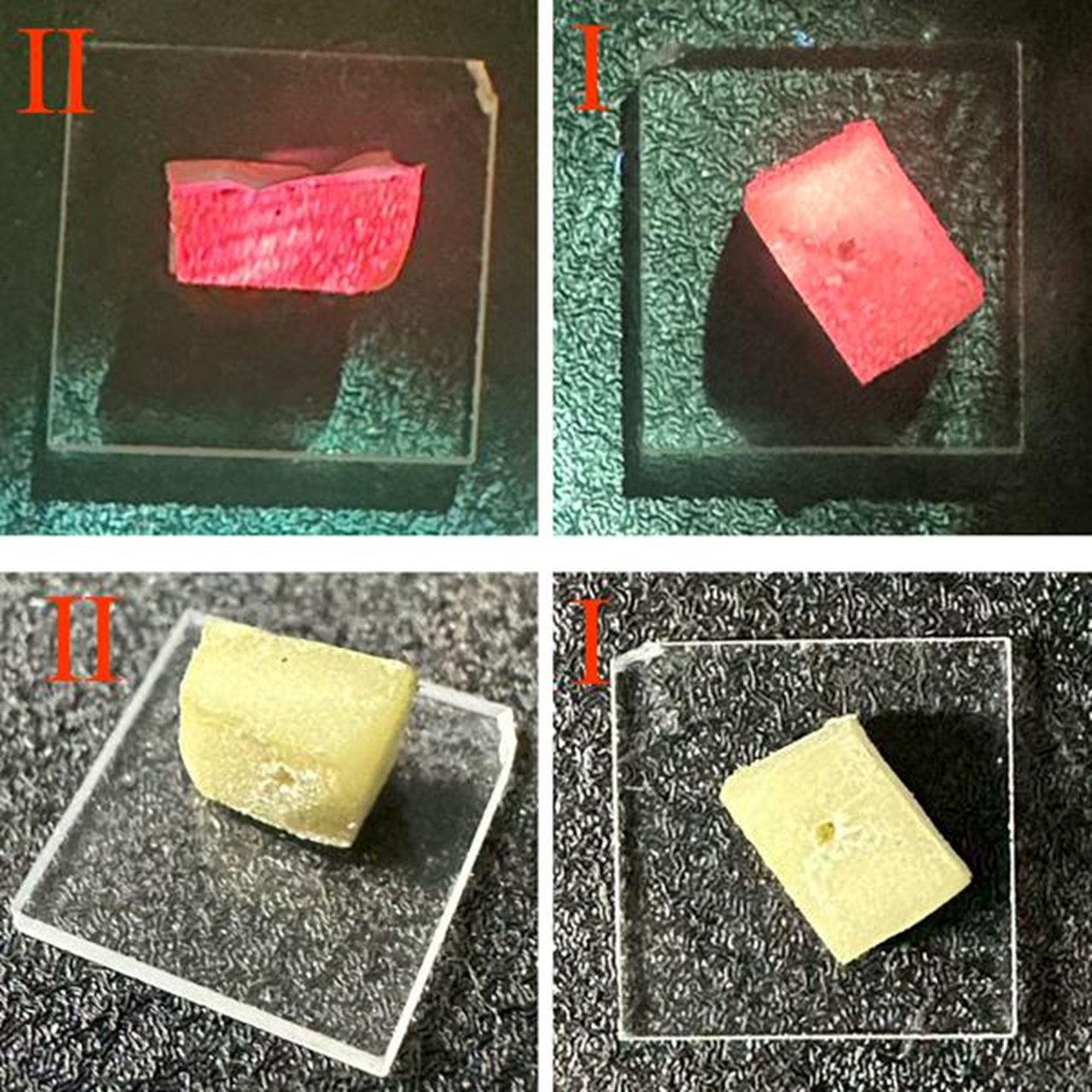
About random lasers
Random lasers are promising for medical imaging and early disease diagnostics because they can produce intense yet diffuse light that penetrates tissue without causing damage. Unlike conventional lasers, which emit light in a narrow, directed beam, a random laser scatters light in many directions. This allows it to illuminate biological samples more evenly and provide detailed information about structures within the tissue.
A few earlier studies have reported biomaterial-based random lasers composed entirely of biological materials, such as abalone shells or coral skeletons combined with chlorophyll.